What is a lead-acid battery?
The Lead-acid battery is one of the oldest types of rechargeable batteries. These batteries were invented in the year 1859 by the French physicist Gaston Plante.
Despite having a small energy-to-volume ratio and a very low energy-to-weight ratio, its ability to supply high surge contents reveals that the cells have a relatively large power-to-weight ratio.

Lead-acid batteries can be classified as secondary batteries. The chemical reactions that occur in secondary cells are reversible. The reactants that generate an electric current in these batteries (via chemical reactions) can be regenerated by passing a current through the battery (recharging).
The chemical process of extracting current from a secondary battery (forward reaction) is called discharging. The method of regenerating active material is called charging.
Sealed Lead Acid Battery
- The sealed lead-acid battery consists of six cells mounted side by side in a single case. The cells are coupled together, and each 2.0V cell adds up to the overall 12.0V capacity of the battery.
- Despite being relatively heavy, lead-acid batteries are still preferred over other lightweight options owing to their ability to deliver large surges of electricity (which is required to start a cold engine in an automobile).
- A completely charged lead-acid battery is made up of a stack of alternating lead oxide electrodes, isolated from each other by layers of porous separators.
- All these parts are placed in a concentrated solution of sulfuric acid. Intercell connectors connect the positive end of one cell to the negative end of the next cell hence the six cells are in series.
Chemical Reaction for Discharging
When the battery is discharged, it acts as a galvanic cell and the following chemical reaction occurs.
Negative:
Pb(s) + HSO4– + H2O(l) –> 2e– + PbSO4(s) + H3O+(aq) (oxidation )
Positive:
PbO2(s) + HSO4–(aq) + 3H3O+(aq) + 2e– –> PbSO4(s) + 5H2O(l) (reduction)
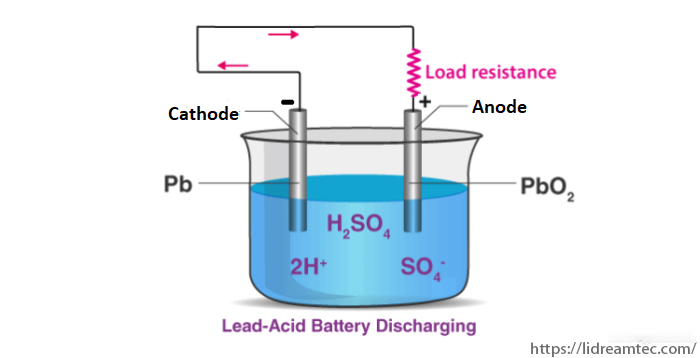
Lead sulfate is formed at both electrodes. Two electrons are also transferred in the complete reaction. The lead-acid battery is packed in a thick rubber or plastic case to prevent leakage of the corrosive sulphuric acid.
Lead Acid Battery Charging
The sulphuric acid existing in the lead discharge battery decomposes and needs to be replaced. Sometimes, the plates change their structure by themselves. Eventually, the battery becomes less efficient and should be charged or changed.
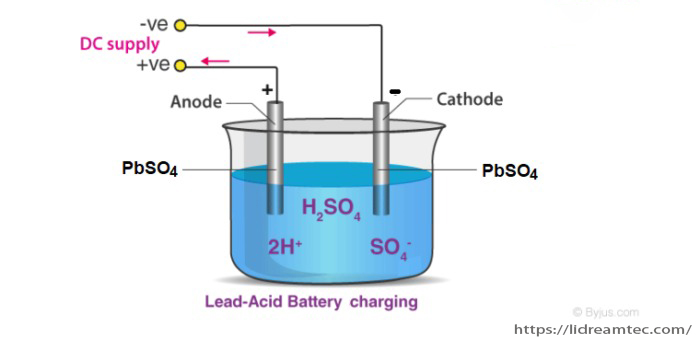
When car batteries spend considerable durations of time in their discharged states, the lead sulfate build-up may become extremely difficult to remove. This is the reason why lead-acid batteries must be charged as soon as possible (to prevent the building up of lead sulfate). Charging of the lead batteries is usually done by providing an external current source.
A plug is inserted which is linked to the lead-acid battery and the chemical reaction proceeds in the opposite direction. In cases where the sulphuric acid in the battery (or some other component of the battery) has undergone decomposition, the charging process may become inefficient. Therefore, it is advisable to check the battery periodically.
Chemical Reaction for Recharging
The chemical reaction that takes place when the lead-acid battery is recharging can be found below.
Negative:
2e– + PbSO4(s) + H3O+(aq) –> Pb(s) + HSO4– + H2O(l) (reduction)
Positive:
PbSO4(s) + 5H2O(l) –> PbO2(s) + HSO4–(aq) + 3H3O+(aq) + 2e– (oxidation)
While recharging, the automobile battery functions like an electrolytic cell. The energy required to drive the recharging comes from an external source, such as an engine of a car. It is also important to note that overcharging of the battery could result in the formation of by-products such as hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. These gases tend to escape from the battery, resulting in the loss of reactants.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q1 What is in a lead acid battery?
The negative plate is made up of lead and the positive plate of lead dioxide in the fully charged state. Concentrated sulphuric acid is the electrolyte, which retains most of the chemical energy.
Q2 How a lead-acid battery is made?
Utilizing lead alloy ingots and lead oxide, the lead battery is made of two chemically dissimilar lead-based plates immersed in a solution of sulphuric acid.
Q3 How do you maintain a lead-acid battery?
Apply a fully saturated charge of 14 to 16 hours to keep lead acid in good condition. If this is not permitted by the charge cycle, give the battery once every few weeks a fully saturated charge.
Q4 Is a lead-acid battery wet or dry?
Different versions of the lead-acid battery are wet cell (flooded), gel cell, and absorbed glass mat (AGM). There are two styles of wet cell; serviceable and maintenance-free. Both are electrolyte-filled and are basically the same.
Q5 What type of battery is lead-acid?
Lead and lead dioxide, the active materials on the plate of the battery, react to lead sulfate in the electrolyte with sulphuric acid. The lead sulfate first forms in a finely divided, amorphous state, and when the battery recharges easily returns to lead, lead dioxide, and sulphuric acid.